
Exchange
a platform for trading cryptocurrencies (e.g., Binance, Kraken)
The comprehensive dictionary for modern trading systems, algorithms, and market microstructure.

a platform for trading cryptocurrencies (e.g., Binance, Kraken)

a specific market on an exchange, such as futures or spot

an abstract pair of traded assets, e.g., BTC/USDT, not tied to a specific exchange

a specific trading pair tied to a specific market (and therefore a specific exchange)

a virtual wallet with assets, tracks balance and positions

a component for generating metrics. Example: difference between opening and closing prices

a component for generating signals based on metrics. Example: if open > close, then buy; if open < close, then sell

takes a signal as input and outputs instructions for the bot

code that knows how to trade based on a signal or without one

an instance of a bot that takes a strategy and portfolio as input and generates trading orders

the main US stock market index reflecting the performance of 500 largest companies. Often used as a baseline reference for analyzing overall market direction.

US technology sector index. Large technology companies have significant influence on the global market.
volatility index, often called the "fear index". High values indicate growing panic and probability of market decline, low values indicate a calm phase.

index reflecting the state of the US industrial sector.

small-cap index, often used to analyze "second-tier" trends and economic rotation.
sector ETF for semiconductors, indicator of sentiment in the technology industry.
volatility of VIX volatility.

percentage of S&P500 stocks trading above their 50-day moving average; important indicator of market overbought/oversold conditions.
percentage of S&P500 stocks above their 200-day moving average; indicator of long-term trend health.

Nasdaq volatility index.

US government bond yields, help assess market sentiment and risks.

US Dollar Index. DXY growth amid declining stocks often indicates flight to "quality".

most popular technical indicators for analyzing trends, momentum, overbought/oversold zones.

market breadth and short-term overbought conditions.

seasonal return variations, "witching Friday" and other calendar effects.
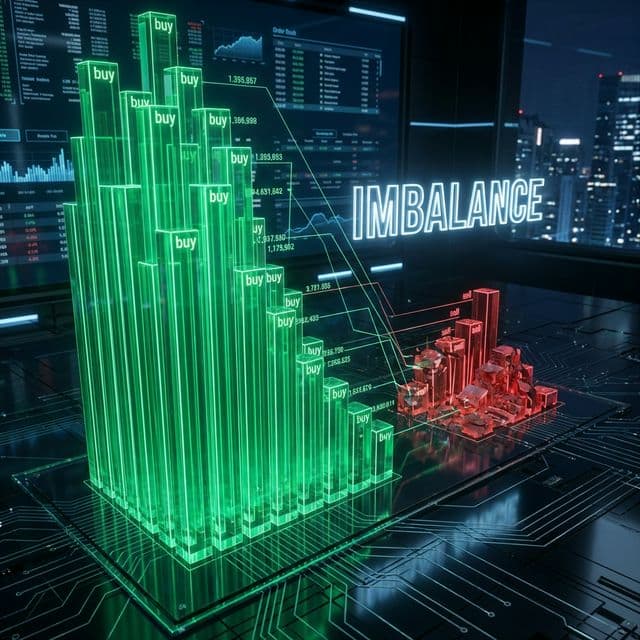

disproportion between the volume of buy orders (bids) and sell orders (asks) in the order book. High imbalance (e.g., bids >> asks) may indicate upcoming demand or preparation for a level "buyout", while the opposite situation indicates selling pressure. In aggregated (cluster) analysis, imbalance is calculated as the relative excess of volume on one side of the order book at a specific price level, or across the entire order book:

opening price of the period

maximum price reached during the period

minimum price reached during the period

closing price of the period

total trading volume during the period

a rectangle showing the difference between opening and closing prices

typically green (or white) for bullish candles (close > open) and red for bearish candles (close < open)

lines extending above and below the body, showing maximum and minimum prices

line from the top of the body to the maximum price

line from the bottom of the body to the minimum price

1, 5, 15, 30 minutes

1, 4 hours

1 day

1 week

1 month

a reversal pattern where a bullish candle completely engulfs the previous bearish candle

a potential signal for a downtrend reversal, characterized by a small body and a long lower shadow

a candle with a very small body, indicating market indecision

an order to buy or sell an asset at the current market price, executed immediately

an order to buy or sell an asset at a specified price or better

an order that activates when a certain price is reached
a combination of stop and limit orders

an order to close a position with profit when a certain price is reached

an order to close a position with a loss to limit potential losses

a dynamic stop loss that follows the price when it moves in a favorable direction

a pair of linked orders where execution of one automatically cancels the other

a large order split into a series of smaller ones to minimize market impact

orders that activate when certain conditions besides price are met

orders that are not displayed in the public order book until they are executed or partially executed. Used to conceal large trading intentions.

orders whose price is tied to a specific market benchmark (e.g., best bid/offer or mid-price) and automatically adjusts as that benchmark changes.

orders that allow a broker or trading system to execute at a price within a specified range or under certain conditions, giving some flexibility in execution to achieve a better price or timing.

the process of executing large orders (block orders) often outside the public order book or through specialized mechanisms to minimize market impact and price slippage.
buying an asset with the expectation of its price increasing

selling an asset with the expectation of its price decreasing
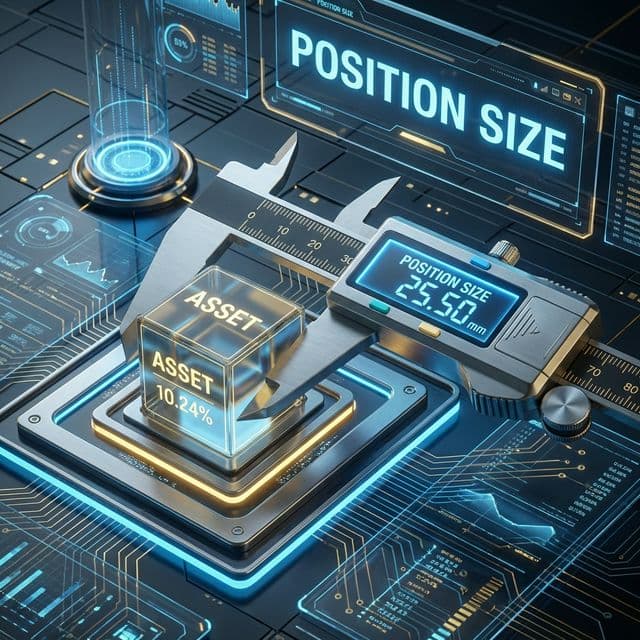

the number of units of an asset in a position
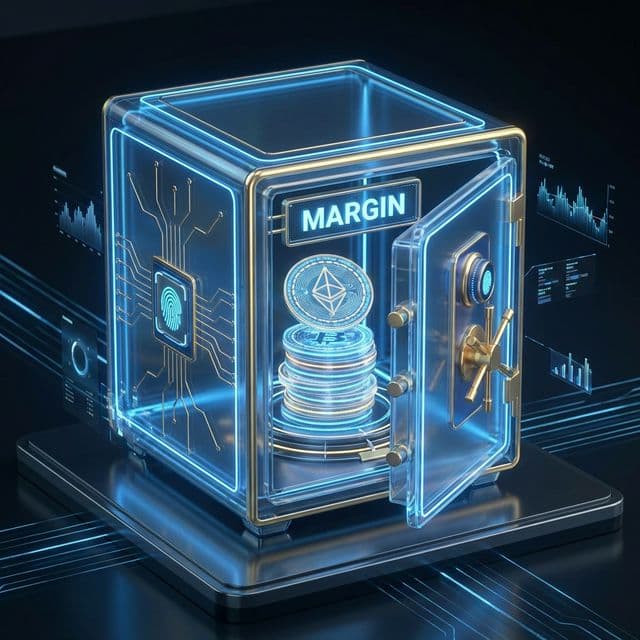

collateral required to open a position with leverage

the ratio between position size and a trader's own funds
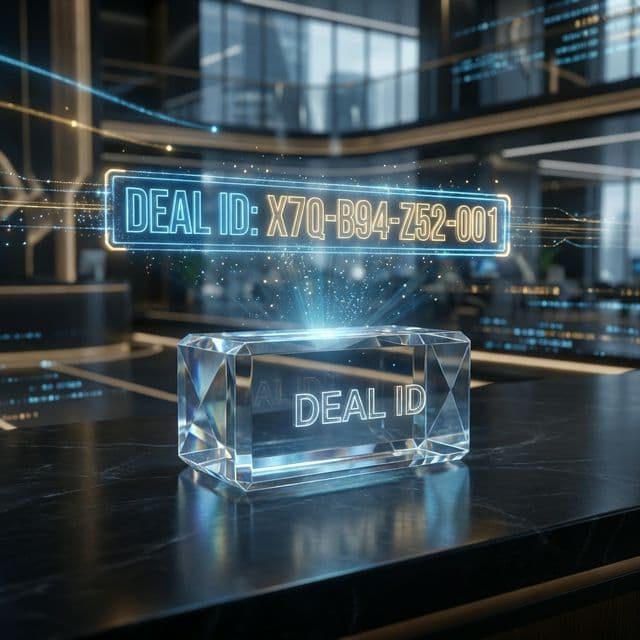

unique identifier
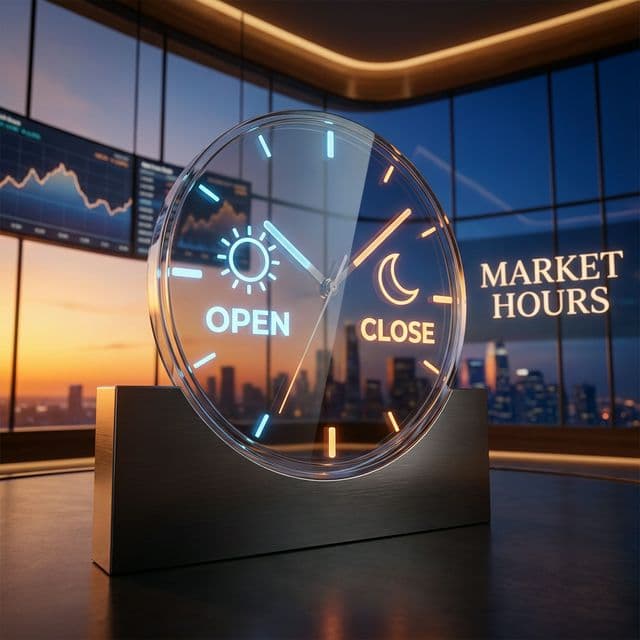

date and time of the first trade within the deal

date and time of the last trade within the deal (if the deal is closed)

duration of the deal (from opening to closing)

open / closed / partially closed / canceled

long / short / arbitrage / spread / other

which bot initiated the deal
which user initiated the deal

symbol(s) of traded instruments (e.g., BTC/USDT)

all trades, positions, and orders included in the deal (including canceled ones)

amount of invested funds (in USDT and base currency)
amount of withdrawn funds (in USDT and base currency)

free-form notes

for filtering and analytics

e.g., if part of a strategy or series of deals

where the deal was executed

an indicator that smooths price fluctuations to identify trends

an oscillator measuring the speed and change of price movements

an indicator showing the relationship between two moving averages
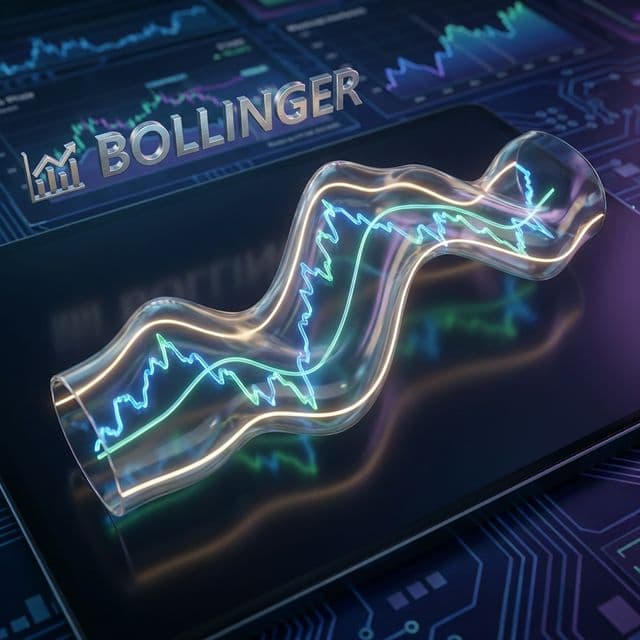

a volatility indicator consisting of a moving average and two standard deviations

OBV (On-Balance Volume), Volume Profile, CVD (Cumulative Volume Delta)
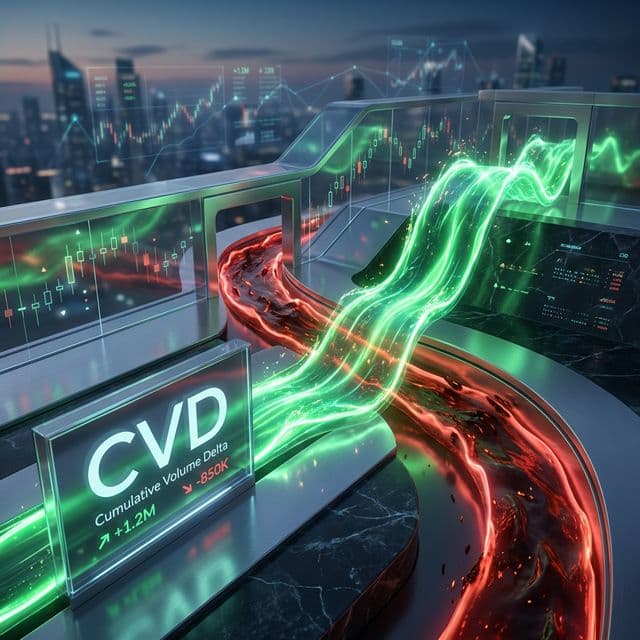

shows the cumulative pressure of buyers (Buy Market Orders) versus sellers (Sell Market Orders) over a selected period, starting from a reference point. Calculated as the running sum of the difference between buy volume at ask prices and sell volume at bid prices for each bar or tick:

Momentum, Rate of Change (ROC)
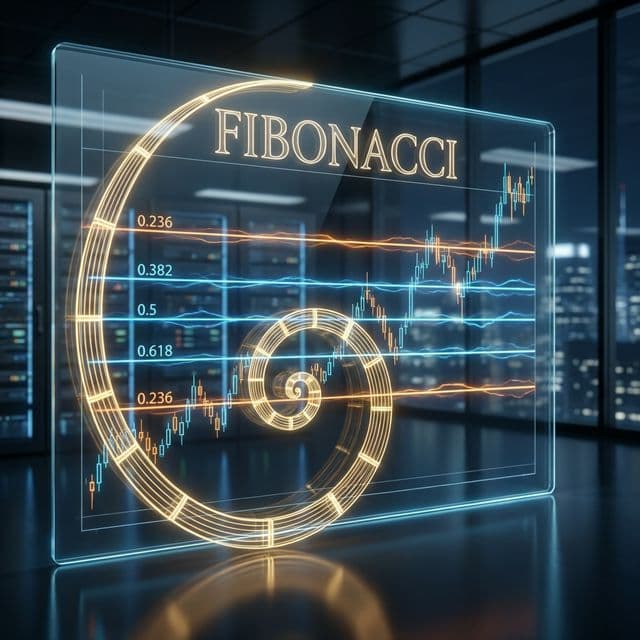

a technical analysis tool based on Fibonacci numbers

a theory of market cycle analysis through wave patterns
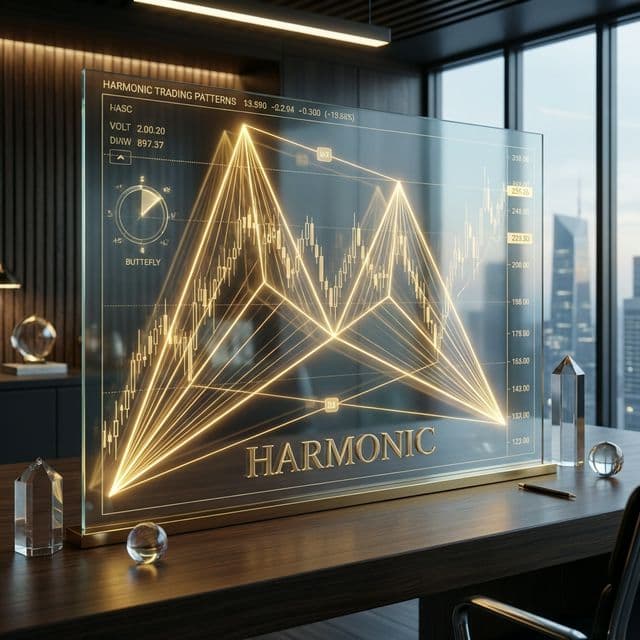

geometric price patterns based on Fibonacci numbers
a method of forecasting future price movements based on studying past price changes and trading volumes. Uses charts, patterns, indicators.

a method of assessing an asset's intrinsic (fair) value by examining economic, financial, and other qualitative and quantitative factors. In cryptocurrencies, this may include analyzing the project, team, technology, tokenomics, community, and overall market conditions.

the assessment of the overall mood or attitude of market participants towards a specific asset or the market as a whole. Sources can include social media, news articles, forums, and surveys. Helps to understand if the market is "bullish" or "bearish" from a crowd psychology perspective.

a market participant who provides liquidity by simultaneously placing buy and sell orders. Main functions:

an individual or institution that supplies buy and sell orders to the market, enhancing liquidity and facilitating smoother trading; can include market makers, banks, or specialized firms.

a market participant who deliberately influences an asset's price to profit from price changes. Main strategies:

a trader who places limit orders, thereby adding liquidity to the orderbook. Usually receives lower fees on exchanges.

a trader who executes existing orders in the book, thereby removing liquidity from the market. Usually pays higher fees.

a market participant who removes liquidity from the market by executing against existing orders in the order book, typically through market orders or aggressive limit orders.

a financial organization (bank, hedge fund, investment fund) trading in large volumes. Has significant resources, information, and can influence the market.

an individual investor trading in relatively small volumes. Usually has limited resources and information.

a market participant who profits from price differences of the same asset on different markets or exchanges. Contributes to price efficiency.

a trader who makes many short-term trades to get small profits from minor price movements. Often uses technical analysis and automated systems.

a market participant with extremely large funds who can significantly influence the price of an asset with their operations.

a measure of how easily an asset can be bought or sold without significantly affecting its price

the number of units of an asset traded during a specific period

the market's ability to absorb large orders without significant price changes

a price level where demand is strong enough to prevent further price decline

a price level where supply is strong enough to prevent further price increases

a sharp price change between two consecutive periods when there is no trading between them

a measure of an asset's price fluctuations

the general direction of an asset's price movement:

the maximum price at which a trader is willing to buy an asset

the minimum price at which a trader is willing to sell an asset

the difference between bid and ask prices

the current price of an asset on an exchange

the average value between bid and ask prices

the minimum price increment by which the price of a financial instrument can change on a trading venue, affecting bid-ask spreads and market liquidity.

the ratio of potential profit to potential loss in a trade

the decline in portfolio value from peak to trough before a new peak

determining the optimal number of asset units to trade considering risk

distributing capital among various assets to reduce risk

a statistical measure of the maximum potential loss of a portfolio over a specific period with a given confidence level (e.g., a 95% VaR of $1000 over 1 day means there is a 95% confidence that losses will not exceed $1000 within one day).

using financial instruments or market strategies to reduce the risk of adverse price movements in an asset. An example is opening a short futures position to hedge a long spot asset position.

an analysis method where a portfolio or strategy is evaluated under hypothetical extreme but plausible market scenarios (e.g., a sharp market crash, liquidity crisis) to understand potential losses and resilience.

automated systems and rules embedded in trading algorithms or platforms to monitor and limit risks in real-time, such as position size limits, maximum loss thresholds, and order frequency controls.

risk management measures applied before order submission to prevent erroneous or risky trades, such as maximum order size limits, price collars, fat-finger checks, and credit checks.

risk management processes and checks performed after trade execution to monitor compliance, detect errors, manage settlement risk, and ensure regulatory reporting.

the ongoing monitoring of trading activity and market behavior to detect and prevent manipulation, fraud, insider trading, and other abusive practices, ensuring market integrity and compliance with regulations.

an emergency mechanism that allows for the immediate shutdown of trading systems or the cancellation of all open orders to prevent further losses or mitigate systemic risk during extreme market events or technical failures.

safeguards and system checks designed to prevent accidental entry of orders with incorrect prices, sizes, or other parameters, such as confirmation prompts, maximum order size limits, and price deviation warnings.

procedures and automated controls to assess a trader's or firm's ability to meet financial obligations before allowing order submission or trade execution, helping to prevent defaults and limit counterparty risk.

a maximum allowable size of a position in a particular asset or market, set by exchanges, regulators, or risk managers to prevent excessive risk exposure and maintain market stability.
a restriction on the number of orders that can be submitted within a specific time period, implemented to prevent excessive trading activity, reduce system load, and mitigate risks associated with high-frequency trading.

a maximum allowable value for a single order or a group of orders, set to prevent excessive exposure or unintended large trades, often enforced by exchanges or risk management systems.

systems and procedures that regulate and monitor who can access trading venues, what types of orders can be submitted, and under what conditions, to prevent unauthorized or risky trading activity.

mechanisms that prevent a trader's own buy and sell orders from matching with each other on an exchange, reducing the risk of wash trades and ensuring genuine market activity.

the overall soundness, fairness, and transparency of a financial market, maintained through regulations, surveillance, and enforcement to ensure that all participants operate on a level playing field and that prices reflect true supply and demand.

the illegal practice of trading financial instruments based on material, non-public information, giving an unfair advantage and undermining market integrity.

the unethical or illegal practice of executing orders on a security for one's own account while taking advantage of advance knowledge of pending orders from clients or the market, typically to profit from the anticipated price movement.

an automated process of adjusting the composition and weights of assets in a portfolio using algorithms to maintain a desired asset allocation or follow a specific investment strategy.

an interface allowing programmatic interaction with an exchange

a protocol for receiving real-time data from an exchange

the maximum number of API requests to an exchange over a specific period

the process of testing a trading strategy on historical data

the process of adjusting strategy parameters to improve results

excessive optimization of a strategy to historical data, which may lead to poor results in the real market

using computer algorithms to automatically execute trading operations

algorithmic trading with very high speed and a large number of trades
mechanisms or rules designed to temporarily halt or slow down high-frequency trading activities during periods of extreme market volatility to prevent flash crashes or systemic disruptions.

high-frequency trading strategies that attempt to predict and react to the order flow of other market participants, often by analyzing patterns in order submissions and cancellations.

a high-frequency trading tactic involving the rapid submission and cancellation of a large number of orders to create confusion or delay in the market, often to gain a competitive advantage.

a high-frequency trading strategy that involves initiating a series of trades to trigger price movements in a specific direction, often to profit from the resulting momentum or to induce other traders to follow.

high-frequency trading tactics where traders place and quickly cancel large orders (spoofing) or place multiple orders at different price levels (layering) to mislead other market participants about supply and demand, often to manipulate prices.

trading algorithms capable of adjusting their parameters or logic in response to changing market conditions in real-time.
the time between sending an order and its execution on an exchange

a strategy using price differences of the same asset on different exchanges or markets to obtain risk-free profit

a short-term trading strategy aimed at making multiple small profits over short time intervals

a medium-term strategy where positions are held from several days to several weeks

a long-term strategy where positions are held from several weeks to several months or even years

using trends and recurring movements on price charts to analyze the general direction of assets

buying and selling assets within one trading day, positions are not carried over to the next day

special algorithms for optimal execution of large orders (TWAP, VWAP, Iceberg)

a type of futures contract without an expiration date, which mimics the spot market but with the possibility of using leverage. The price is pegged to the spot price index through a funding rate mechanism.

regular payments between holders of long and short positions in perpetual futures. If the rate is positive, longs pay shorts; if negative, shorts pay longs. This helps keep the futures price close to the spot price.

represents the total number of open contracts (futures/options) that have not been closed or exercised. Calculated as the total number of active open positions:

the minimum amount of funds a trader must deposit to open a leveraged position. Calculated as a percentage of the total position size.

the minimum margin level that must be maintained in an account after opening a position. If the account balance falls below this level, a margin call or liquidation occurs.

the forced closure of a trader's position by the exchange when their margin falls below the maintenance margin level. This is done to prevent further losses that could exceed the trader's account funds.

a contract giving the buyer the right (but not the obligation) to buy the underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) within a certain period or on a specific date (expiration date).

a contract giving the buyer the right (but not the obligation) to sell the underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) within a certain period or on a specific date (expiration date).
the price at which the option holder can buy (for a call option) or sell (for a put option) the underlying asset.

the date after which the option contract becomes invalid.

a set of metrics used to measure various aspects of an option position's risk:
the study of the process and outcomes of exchanging assets under explicit trading rules, focusing on how specific trading mechanisms affect price formation, liquidity, transaction costs, and market efficiency.
analysis of the sequence of orders entering the market

the ratio of volumes on the buy and sell sides

price change resulting from the execution of a large order

private exchanges or trading venues where financial instruments are traded without displaying quotes publicly, allowing large blocks of securities to be bought or sold anonymously to minimize market impact.

the dispersion of trading volume across multiple trading venues, exchanges, or platforms, which can result in reduced liquidity in any single venue and potentially wider spreads.

systematic approaches used by market makers to provide liquidity while managing risk and generating profit, typically involving simultaneous placement of buy and sell orders at different price levels with the goal of capturing the spread.

a measure of the volume of orders at different price levels in the order book, indicating the market's ability to absorb large trades without significant price impact; deeper order books generally suggest higher liquidity.

the process of combining liquidity from multiple sources, such as different exchanges or trading venues, to provide traders with better pricing, deeper order books, and improved execution quality.

the core system of a trading venue or exchange that automatically matches buy and sell orders based on price, time, and other criteria, ensuring fair and efficient trade execution.

studying trading volumes at different price levels

the mathematical expectation of a trading strategy's result

the largest percentage decrease in capital from peak to trough

a measure of investment efficiency considering risk

a risk-adjusted return ratio that considers drawdowns

a measure of trading strategy effectiveness

a measure of trading strategy sensitivity to a market index

the ratio of profit to maximum drawdown

the optimal proportion of capital for trading

psychological biases affecting trading decisions. Examples:

a systematic record of all trades and their analysis

placing trading servers in close proximity to exchange servers

utilizing the time difference in receiving market data

a high-frequency trading strategy that exploits tiny time differences in market data transmission across exchanges or venues to profit from price discrepancies before they are corrected.

optimizing network connections to minimize delays

tools for tracking the operation of trading algorithms in real-time

a system that automatically routes orders to various trading venues (exchanges, dark pools, etc.) to achieve the best execution based on price, speed, or other criteria. Also known as Smart Order Routing.
the process of directing orders to different trading venues, exchanges, or liquidity providers to achieve optimal execution based on factors such as price, speed, and available liquidity.

a regulatory requirement or system feature designed to prevent orders from being executed at inferior prices when better prices are available on other trading venues, ensuring best execution for traders.

the obligation of brokers and trading systems to execute client orders on the most favorable terms available, considering factors such as price, speed, likelihood of execution, and overall cost.

a process of evaluating and measuring the costs associated with trading activities, including explicit costs (commissions, fees) and implicit costs (slippage, market impact), to assess execution quality and optimize trading strategies.

techniques and tools used to minimize the difference between the expected and actual execution price of a trade, such as setting slippage limits, using limit orders, or employing advanced execution algorithms.

the process by which a trading system or exchange compares and pairs buy and sell quotes/orders based on price, time, and other criteria to facilitate trade execution.

the practice of limiting the rate at which orders can be submitted to a trading system or exchange, typically to prevent system overload, reduce risk, and ensure fair access for all participants.

a confirmation message sent by a trading system or exchange to notify the sender that an order has been received and accepted for processing, providing assurance of order status.

a notification sent by a trading system or exchange to inform the trader that an order, or part of it, has been executed, including details such as price, quantity, and time of execution.

a real-time copy of trade and order messages sent to a third-party system (such as risk management or compliance) for monitoring, auditing, or backup purposes.

a periodic message exchanged between systems to confirm connectivity and session health, ensuring that communication channels remain active and responsive.

the processes and controls used to establish, maintain, and terminate communication sessions between trading systems, including authentication, authorization, and recovery from interruptions.

strategies and procedures for restoring trading operations and data after a major system failure, cyberattack, or other catastrophic event, ensuring business continuity and regulatory compliance.

a network communication method that allows data to be sent from one source to multiple recipients simultaneously, commonly used for distributing market data feeds with low latency.

the foundational suite of communication protocols used for interconnecting network devices on the internet, providing reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of data.

a protocol providing full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection, widely used for real-time data streaming in trading platforms and exchanges.

a web service interface based on Representational State Transfer principles, enabling programmatic access to trading and market data using standard HTTP methods.

a high-performance, open-source remote procedure call (RPC) framework that uses HTTP/2 for transport and Protocol Buffers for efficient serialization, suitable for low-latency trading system integration.

a technology that enables traders to place orders directly into the order books of exchanges, bypassing intermediaries and allowing for faster execution, lower latency, and greater control over trading strategies.

the Financial Information eXchange protocol, a widely used electronic communications protocol for real-time exchange of securities transactions and market data between financial institutions.

a high-performance binary encoding protocol developed as an extension to FIX, designed to reduce bandwidth and latency for market data and trading messages.

a proprietary high-speed trading and market data protocol used by the Moscow Exchange, optimized for low-latency electronic trading environments.

a decentralized exchange operating without a central intermediary

an automated market maker used in DEXs

a pool of liquidity in decentralized protocols

temporary value loss when providing liquidity in AMMs

the process of earning rewards (often in the form of additional tokens) for providing liquidity or staking cryptocurrencies in DeFi protocols.

the process of holding cryptocurrency in a wallet or on a special platform to support blockchain operations (e.g., validating transactions in Proof-of-Stake networks) and earn rewards.

a type of yield farming where users receive protocol governance tokens in exchange for providing liquidity.

tokens that represent an asset from another blockchain. For example, Wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC) is an ERC-20 token whose value is pegged to Bitcoin, allowing BTC to be used in the Ethereum DeFi ecosystem.

services that supply smart contracts with real-world data (e.g., currency exchange rates, sports event outcomes) necessary for their correct operation.

a special type of uncollateralized loans in DeFi that must be borrowed and repaid within a single blockchain transaction. Used for arbitrage, refinancing, and other complex operations.

the maximum value that miners (in Proof-of-Work networks) or validators (in Proof-of-Stake networks) can extract from block production beyond the standard block reward and transaction fees, by including, excluding, or reordering transactions within a block.

the process of creating new tokens. This can occur according to a predefined algorithm (e.g., in Proof-of-Stake during staking) or by the decision of the project team.

the process of gradually unlocking tokens distributed to the project team, advisors, or early investors. Usually occurs on a specific schedule to prevent a sharp drop in token price.

the process of permanently removing a certain number of tokens from circulation. Used to reduce the total supply of tokens, which can potentially increase their value.